快速 Diff 算法
快速 Diff 算法最早应用于 ivi 和 inferno 这两个框架,在 DOM 操作的各个方面,这个算法性能都要稍优于 Vue.js 2 所采用的双端 Diff 算法。
相同的前置元素和后置元素
纯文本 Diff 算法
不同于简单 Diff 算法和双端 Diff 算法,快速 Diff 算法包含预处理步骤,这借鉴了纯文本 Diff 算法的思路。在纯文本 Diff 算法中,存在对两段文本进行预处理的过程。
例如,在两段文本进行 Diff 之前,可以对它们进行全等比较:
if(text1 === text2) return
这也成为快捷路径。如果两端文本内容相等,就无需进入核心 Diff 算法的步骤了。除此之外,Diff 算法还会处理两段文本的前缀和后缀:
TEXT1: I use vue for app development
TEXT2: I use react for app development
TEXT1:vue
TEXT2:react
========================================
TEXT1: I like you
TEXT2: I like you too
TEXT1:
TEXT2:too
========================================
TEXT1: I like you too
TEXT2: I like you
TEXT1:too
TEXT2:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
这么做的好处是,在特定情况下我们能够轻松判断文本的插入和删除。
快速 Diff 算法
快速 Diff 算法借鉴了纯文本 Diff 算法中的预处理的步骤。它会先处理一下新旧子节点里相同的前置节点和后置节点。
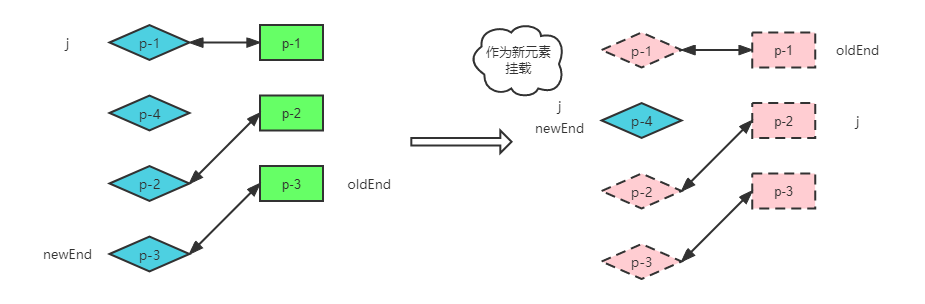
处理完前置和后置节点之后,新子节点未处理的部分 [ j, newEnd ] 区间内的节点,作为新元素挂载。
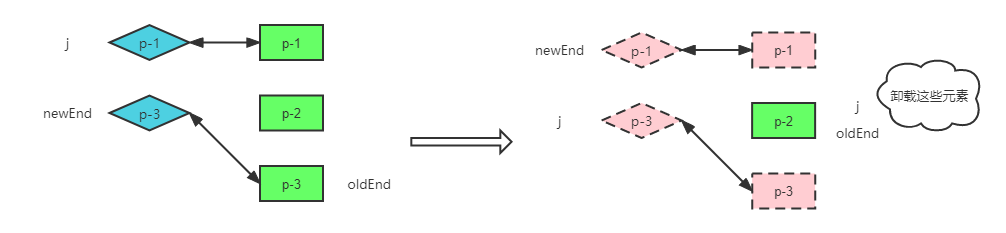
处理完前置和后置节点之后,旧子节点未处理的部分 [ j, oldEnd ] 区间内的节点要卸载。
function patchKeyedChildren(n1, n2, container) {
const newChildren = n2.children
const oldChildren = n1.children
// 更新相同的前缀节点
// 索引 j 指向新旧两组子节点的开头
let j = 0
let oldVNode = oldChildren[j]
let newVNode = newChildren[j]
// while 循环向后遍历,直到遇到拥有不同 key 值的节点为止
while (oldVNode.key === newVNode.key) {
// 调用 patch 函数更新
patch(oldVNode, newVNode, container)
j++
oldVNode = oldChildren[j]
newVNode = newChildren[j]
}
// 更新相同的后缀节点
// 索引 oldEnd 指向旧的一组子节点的最后一个节点
let oldEnd = oldChildren.length - 1
// 索引 newEnd 指向新的一组子节点的最后一个节点
let newEnd = newChildren.length - 1
oldVNode = oldChildren[oldEnd]
newVNode = newChildren[newEnd]
// while 循环向前遍历,直到遇到拥有不同 key 值的节点为止
while (oldVNode.key === newVNode.key) {
// 调用 patch 函数更新
patch(oldVNode, newVNode, container)
oldEnd--
newEnd--
oldVNode = oldChildren[oldEnd]
newVNode = newChildren[newEnd]
}
// 满足条件,则说明从 j -> newEnd 之间的节点应作为新节点插入
// j > oldEnd:旧节点全部被处理完毕
if (j > oldEnd && j <= newEnd) {
// 锚点的索引
const anchorIndex = newEnd + 1
// 锚点元素
const anchor = anchorIndex < newChildren.length ? newChildren[anchorIndex].el : null
// 采用 while 循环,调用 patch 函数逐个挂载新增的节点
while (j <= newEnd) {
patch(null, newChildren[j++], container, anchor)
}
} else if (j > newEnd && j <= oldEnd) {
// j -> oldEnd 之间的节点应该被卸载
// j > newnd:新节点全部被处理完毕
while (j <= oldEnd) {
unmount(oldChildren[j++])
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
移动操作判断
之前介绍了快速 Diff 算法的预处理过程,即处理相同的前置节点和后置节点。
但是,之前的例子比较理想化,总是假定新旧子节点有一组会被全部处理完毕。在这种情况下,只需要简单地挂载、卸载节点即可。
我们使用不同的一组新旧子节点来进行说明:
经过预处理之后,无论是新的一组子节点还是旧的一组子节点都有节点未处理。我们需要对此进一步处理:
- 判断是否有节点需要移动,以及应该如何移动
- 找出那些需要被添加或移除的节点
if (j > oldEnd && j <= newEnd) {
// 只有需要新增的节点
} else if (j > newEnd && j <= oldEnd) {
// 只有需要卸载的节点
} else {
// 处理非理想情况
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
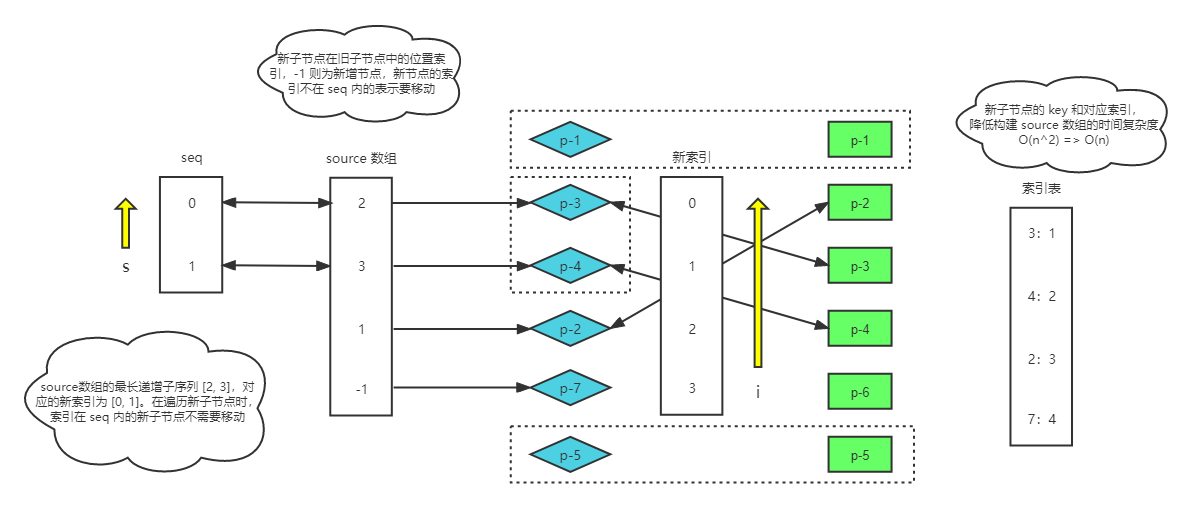
souce 数组
首先,我们需要构建一个 source 数组,它的长度为新的一组子节点中剩余未处理节点的数量,source 数组用来存储新的一组子节点中的节点在旧的一组子节点中的位置索引,后面将会使用它计算出一个最长递增子序列,并用于辅助完成 DOM 的移动操作。
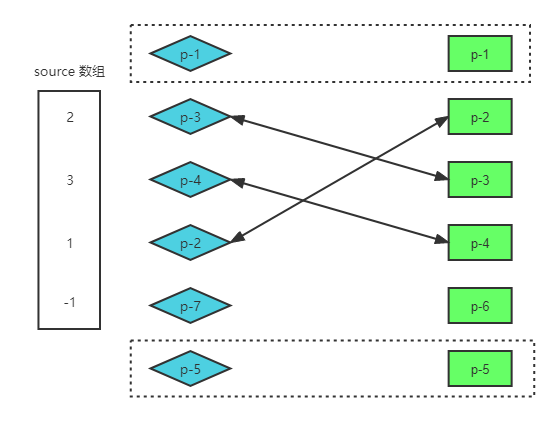
当遍历剩余的新子节点时,如果这个节点在 source 中对应的值为 -1,表示这个节点无法在旧子节点数组中找到可复用的节点,这就是一个需要新增的节点。
构建 souce 数组
if (j > oldEnd && j <= newEnd) {
// 只有需要新增的节点
} else if (j > newEnd && j <= oldEnd) {
// 只有需要卸载的节点
} else {
const count = newEnd - j + 1 // 新的一组子节点中剩余未处理节点的数量
const source = new Array(count)
source.fill(-1)
// oldStart 和 newStart 分别未起始索引,即 j
const oldStart = j;
const newStart = j;
// 遍历旧的一组子节点
for(let i = oldStart; i <= oldEnd; i++) {
const oldVNode = oldChildren[i]
// 遍历新的一组子节点
for(let k = newStart; k <= newEnd; k++) {
const newVNode = newChildren[i]
// 找到拥有相同 key 的可复用节点
if(oldVNode.key === newVNode.key) {
// 调用 patch 进行更新
patch(oldVNode, newVNode, container)
// 最后填充 source 数组
source[k - newStart] = i
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
source 记录的是剩余未处理的新子节点在旧子节点当中的可复用节点,索引记录的下标要减去 newStart
索引表降低时间复杂度
🚀 当前的双层 for 循环的时间复杂度未 O(n^2),我们可以利用索引表来把时间复杂度降低到 O(n)
if (j > oldEnd && j <= newEnd) {
// 只有需要新增的节点
} else if (j > newEnd && j <= oldEnd) {
// 只有需要卸载的节点
} else {
const count = newEnd - j + 1 // 新的一组子节点中剩余未处理节点的数量
const source = new Array(count)
source.fill(-1)
// oldStart 和 newStart 分别未起始索引,即 j
const oldStart = j;
const newStart = j;
// 🔥 构建索引表
const keyIndex = {}
for(let i = newStart; i <= newEnd; i++) {
keyIndex[newChildren[i].key] = i
}
// 遍历旧的一组子节点中剩余未处理的节点
for(let i = oldStart; i <= oldEnd; i++) {
oldVNode = oldChildren[i]
// 通过索引表快速找到新的一组子节点中可复用节点的位置
const k = keyIndex[oldVNode.key]
if (typeof k !== 'undefined') {
newVNode = newChildren[k]
// 调用 patch 函数完成更新
patch(oldVNode, newVNode, container)
// 🚀 填充 source 数组
source[k - newStart] = i
} else {
// 没找到,卸载
unmount(oldVNode)
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
构建 source 数组
索引表存着剩余未处理子节点,键值分别为节点 key 和新子节点数组当中的索引:
keyIndex: Record<key, newIdx>
在遍历旧子节点数组的过程中,如果无法在新子节点列表中找到可复用节点,则卸载该节点
如果找到了可复用节点,则把新子节点对应的旧子节点的索引记录在 source 数组当中
节点移动判断
在遍历旧节点的过程中,如果找到了可复用节点,需要判断这个节点要不要移动。
如果在遍历过程中遇到的索引值呈现递增趋势,则说明不需要移动节点,反之则需要。
同时我们还需要一个数量标识,代表已经更新过的节点,更新过的节点数量应该小于新的一组子节点中需要更新的节点数量
count = newEnd - newStart + 1一旦前者超过了后者,则说明这些节点都是多余的旧节点,应该将它们卸载。
for(let i = oldStart; i <= oldEnd; i++) {
oldVNode = oldChildren[i]
const k = keyIndex[oldVNode.key]
if (typeof k !== 'undefined') {
newVNode = newChildren[k]
patch(oldVNode, newVNode, container)
source[k - newStart] = i
// 判断是否需要移动
if (k < pos) {
moved = true
} else {
pos = k
}
} else {
// 旧节点没有对应的可复用新节点,卸载其
unmount(oldVNode)
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
const count = newEnd - j + 1 // 新的一组子节点中剩余未处理节点的数量
// ...
for(let i = oldStart; i <= oldEnd; i++) {
oldVNode = oldChildren[i]
// 如果更新过的节点数量小于需要更新的节点数量,则执行更新
if (patched < count) {
const k = keyIndex[oldVNode.key]
// 有可复用新节点,执行更新
if (typeof k !== 'undefined') {
newVNode = newChildren[k]
patch(oldVNode, newVNode, container)
patched++
source[k - newStart] = i
// 判断是否需要移动
if (k < pos) {
// 标记 moved 为 true,表示需要移动
moved = true
} else {
pos = k
}
} else {
// 没有对应的可复用新节点,卸载
unmount(oldVNode)
}
} else {
// 如果更新过的旧节点数量超过了需要更新的节点数量,则卸载它们
unmount(oldVNode)
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
如何移动元素
在上一节中,我们实现了两个目标:
- 判断是否需要进行 DOM 移动操作。我们创建了遍历 moved 作为标识,当它的值为 true 时,说明需要进行 DOM 移动操作。
- 构建 source 数组。该数组的长度等于新的一组子节点去掉相同的前置/后置节点后,剩余未处理节点的数量。source 数组中存储着新的一组子节点中在旧的一组子节点中的位置,后面我们会根据 source 数组计算出一个最长递增子序列,用于 DOM 移动操作。
最长递增子序列
目前的 source 数组为:[2, 3, 1, -1]。它表示新子节点在旧子节点中的位置,通过最长递增子序列的计算,我们可以发现 [2, 3] 也就是前面两个新子节点可以保持不移动,这样我们就得到一个最大的不需要移动的新节点的索引数组 [0, 1]
if(moved) {
// 计算 [2, 3, 1, -1] 最长递增子序列
const seq = lis(source) // [0, 1]
}
2
3
4
🚀 在新的一组子节点中,重新编号后的索引值为 0 和 1 的这两个节点在更新前后顺序没有变化。换句话说,重新编号之后,索引值为 0 和 1 的节点不需要移动。
移动与挂载
从后往前遍历新的子节点数组:
- 如果该节点没有可复用的旧节点,也就是说,source 数组里对应下标的值为 -1,那么这个节点就是需要挂载的新节点。
- seq 是递增的,遍历新子节点是从后往前的,那么如果新节点下标和 seq 未遍历的最后这个值不等,也就是说这个新节点的下标不存在于 seq 当中。则需要移动该节点。
- 如果该节点的新下标存在于 seq 中,则该节点不需要移动。
if (moved) {
const seq = lis(source)
// s 指向最长递增子序列的最后一个值
let s = seq.length - 1
let i = count - 1
for (i; i >= 0; i--) {
if (source[i] === -1) {
// 说明索引为 i 的节点是全新的节点,应该将其挂载
// 该节点在新 children 中的真实位置索引
const pos = i + newStart
const newVNode = newChildren[pos]
// 该节点下一个节点的位置索引
const nextPos = pos + 1
// 锚点
const anchor = nextPos < newChildren.length
? newChildren[nextPos].el
: null
// 挂载 patch
patch(null, newVNode, container, anchor)
} else if (i !== seq[j]) {
// 说明该节点需要移动
// 该节点在新的一组子节点中的真实位置索引
const pos = i + newStart
const newVNode = newChildren[pos]
// 该节点下一个节点的位置索引
const nextPos = pos + 1
// 锚点
const anchor = nextPos < newChildren.length
? newChildren[nextPos].el
: null
// 移动 insert
insert(newVNode.el, container, anchor)
} else {
// 当 i === seq[j] 时,说明该位置的节点不需要移动
// 并让 s 指向下一个位置
s--
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
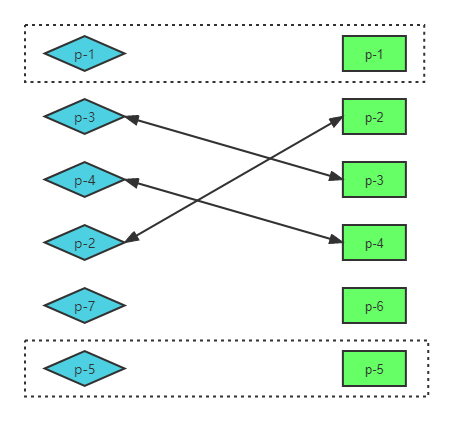
旧 [1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 5] => 新 [1, 3, 4, 2, 7, 5]
预处理,去除相同的前置和后置节点。
[1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 5] <==> [2, 3, 4, 6]
遍历旧节点,构建 source 数组,没有找到可复用的 p-6,卸载该节点。
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5] <==> [2, 3, 4]
moved 为 true,开始移动操作。
p-7 在 source 数组当中的下标为 -1,没有可复用旧节点,挂载 p-7 节点到 p-5 前面。
[1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 5] <==> [2, 3, 4, 7]
p-2 在 source 数组当中的下标为 1。p-2 的新索引 i 为 2,与 seq[1] 即 1 不等,要移动到 p-7 前面。
[1, 3, 4, 2, 7, 5] <==> [3, 4, 2, 7]
p-4 在 source 数组当中的下标为 3。p-4 的新索引 i 为 1,与 seq[1] 即 1 相等,不用移动。
[1, 3, 4, 2, 7, 5] <==> [3, 4, 2, 7]
p-3 在 source 数组当中的下标为 2。p-4 的新索引 i 为 0,与 seq[0] 即 0 相等,不用移动。
[1, 3, 4, 2, 7, 5] <==> [3, 4, 2, 7]
处理完毕:[1, 3, 4, 2, 7, 5]
整个快速 Diff 过程中一共有三次 DOM 操作,分别是卸载 p-6、挂载 p-7 和移动 p-2。
总结
🔥 快速 Diff 算法在实测中性能最优。
它借鉴了文本 Diff 中的预处理思路,先处理新旧两组节点中相同的前置节点和相同的后置节点。
当前置节点和后置节点全部处理完毕,如果无法简单地通过挂载新节点或者卸载已经不存在的旧节点来完成更新,则需要根据节点的索引关系,构造出一个最长递增子序列。最长递增子序列所指向的节点即为不需要移动的节点。
function patchChildren(n1, n2, container) {
if (typeof n2.children === 'string') {
if (Array.isArray(n1.children)) {
n1.children.forEach((c) => unmount(c))
}
setElementText(container, n2.children)
} else if (Array.isArray(n2.children)) {
patchKeyedChildren(n1, n2, container)
} else {
if (Array.isArray(n1.children)) {
n1.children.forEach(c => unmount(c))
} else if (typeof n1.children === 'string') {
setElementText(container, '')
}
}
}
function patchKeyedChildren(n1, n2, container) {
const newChildren = n2.children
const oldChildren = n1.children
// 更新相同的前缀节点
// 索引 j 指向新旧两组子节点的开头
let j = 0
let oldVNode = oldChildren[j]
let newVNode = newChildren[j]
// while 循环向后遍历,直到遇到拥有不同 key 值的节点为止
while (oldVNode.key === newVNode.key) {
// 调用 patch 函数更新
patch(oldVNode, newVNode, container)
j++
oldVNode = oldChildren[j]
newVNode = newChildren[j]
}
// 更新相同的后缀节点
// 索引 oldEnd 指向旧的一组子节点的最后一个节点
let oldEnd = oldChildren.length - 1
// 索引 newEnd 指向新的一组子节点的最后一个节点
let newEnd = newChildren.length - 1
oldVNode = oldChildren[oldEnd]
newVNode = newChildren[newEnd]
// while 循环向前遍历,直到遇到拥有不同 key 值的节点为止
while (oldVNode.key === newVNode.key) {
// 调用 patch 函数更新
patch(oldVNode, newVNode, container)
oldEnd--
newEnd--
oldVNode = oldChildren[oldEnd]
newVNode = newChildren[newEnd]
}
// 满足条件,则说明从 j -> newEnd 之间的节点应作为新节点插入
if (j > oldEnd && j <= newEnd) {
// 锚点的索引
const anchorIndex = newEnd + 1
// 锚点元素
const anchor = anchorIndex < newChildren.length ? newChildren[anchorIndex].el : null
// 采用 while 循环,调用 patch 函数逐个挂载新增的节点
while (j <= newEnd) {
patch(null, newChildren[j++], container, anchor)
}
} else if (j > newEnd && j <= oldEnd) {
// j -> oldEnd 之间的节点应该被卸载
while (j <= oldEnd) {
unmount(oldChildren[j++])
}
} else {
// 构造 source 数组
const count = newEnd - j + 1 // 新的一组子节点中剩余未处理节点的数量
const source = new Array(count)
source.fill(-1)
const oldStart = j
const newStart = j
let moved = false
let pos = 0
const keyIndex = {}
for(let i = newStart; i <= newEnd; i++) {
keyIndex[newChildren[i].key] = i
}
let patched = 0
for(let i = oldStart; i <= oldEnd; i++) {
oldVNode = oldChildren[i]
if (patched < count) {
const k = keyIndex[oldVNode.key]
if (typeof k !== 'undefined') {
newVNode = newChildren[k]
patch(oldVNode, newVNode, container)
patched++
source[k - newStart] = i
// 判断是否需要移动
if (k < pos) {
moved = true
} else {
pos = k
}
} else {
// 没找到
unmount(oldVNode)
}
} else {
unmount(oldVNode)
}
}
if (moved) {
const seq = lis(source)
// s 指向最长递增子序列的最后一个值
let s = seq.length - 1
let i = count - 1
for (i; i >= 0; i--) {
if (source[i] === -1) {
// 说明索引为 i 的节点是全新的节点,应该将其挂载
// 该节点在新 children 中的真实位置索引
const pos = i + newStart
const newVNode = newChildren[pos]
// 该节点下一个节点的位置索引
const nextPos = pos + 1
// 锚点
const anchor = nextPos < newChildren.length
? newChildren[nextPos].el
: null
// 挂载
patch(null, newVNode, container, anchor)
} else if (i !== seq[j]) {
// 说明该节点需要移动
// 该节点在新的一组子节点中的真实位置索引
const pos = i + newStart
const newVNode = newChildren[pos]
// 该节点下一个节点的位置索引
const nextPos = pos + 1
// 锚点
const anchor = nextPos < newChildren.length
? newChildren[nextPos].el
: null
// 移动
insert(newVNode.el, container, anchor)
} else {
// 当 i === seq[j] 时,说明该位置的节点不需要移动
// 并让 s 指向下一个位置
s--
}
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149