弹性布局
📗 Flex 是 Flexible Box 的缩写,意为"弹性布局",可以轻松的控制元素排列、对齐和顺序的控制。
现在的终端类型非常多,使用弹性盒模型可以让元素在不同尺寸终端控制尺寸。
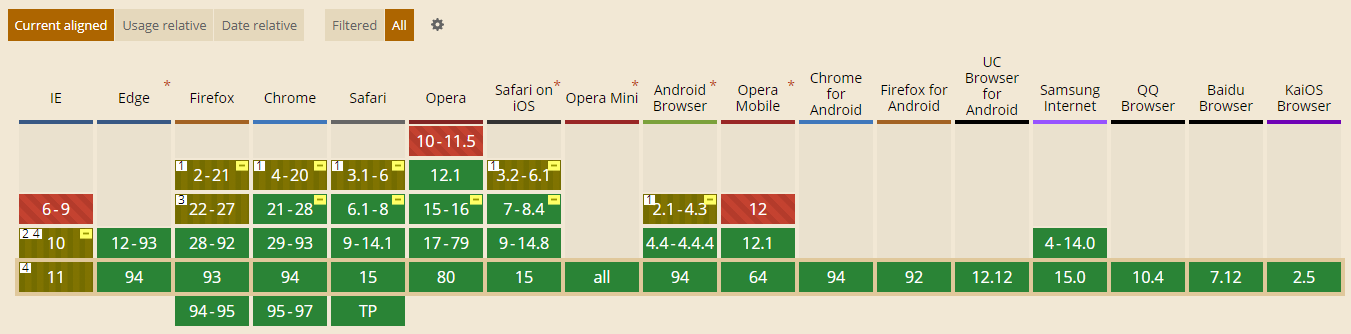
兼容性
下面是FLEX系统兼容性数据,在 https://caniuse.com/ (opens new window)在新窗口打开网站查看,绝大多数设备尤其是移动端都很好的支持FLEX,所以可以放心使用。
弹性盒子
声明定义
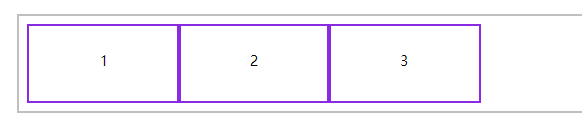
📗 容器盒子里面包含着容器元素,使用 display:flex 或 display:inline-flex 声明为弹性盒子。
声明块级弹性盒子
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
article {
height: 150px;
margin-left: 100px;
margin-top: 100px;
outline: solid 5px silver;
display: flex;
padding: 20px;
}
article div {
outline: solid 5px blueviolet;
text-align: center;
font-size: 28px;
line-height: 5em;
width: 300px;
}
</style>
<article>
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
</article>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
声明内联级弹性盒子
article {
display: inline-flex
}
2
3
flex-direction
📗 用于控制盒子元素排列的方向。
| 值 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| row | 从左到右水平排列元素(默认值) |
| row-reverse | 从右向左排列元素 |
| column | 从上到下垂直排列元素 |
| column-reverse | 从下到上垂直排列元素 |
row-reverse

<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
body {
margin: 100px;
font-size: 14px;
color: #555;
}
article {
width: 500px;
border: solid 5px silver;
display: flex;
box-sizing: border-box;
padding: 10px;
flex-direction: row-reverse;
}
article * {
border: solid 5px blueviolet;
padding: 10px;
margin: 10px;
}
</style>
<article>
<h4>A</h4>
<span>B</span>
<p>C</p>
</article>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
column-reverse

article {
flex-direction: column-reverse;
}
2
3
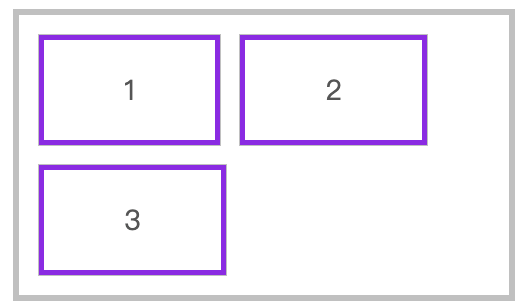
flex-wrap
📗 flex-wrap 属性规定flex容器是单行或者多行,同时横轴的方向决定了新行堆叠的方向。
| 选项 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| nowrap | 元素不拆行或不拆列(默认值) |
| wrap | 容器元素在必要的时候拆行或拆列。 |
| wrap-reverse | 容器元素在必要的时候拆行或拆列,但是以相反的顺序 |
行元素换行
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
outline: solid 1px silver;
padding: 10px;
margin: 10px;
}
head {
display: block;
}
body {
font-size: 14px;
color: #555;
}
article {
width: 500px;
border: solid 5px silver;
box-sizing: border-box;
padding: 10px;
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
/* 指定弹性盒子超出换行 */
flex-wrap: wrap;
}
article div {
border: solid 5px blueviolet;
padding: 30px 80px;
margin: 10px;
text-align: center;
font-size: 28px;
}
</style>
<article>
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
</article>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
水平排列反向换行
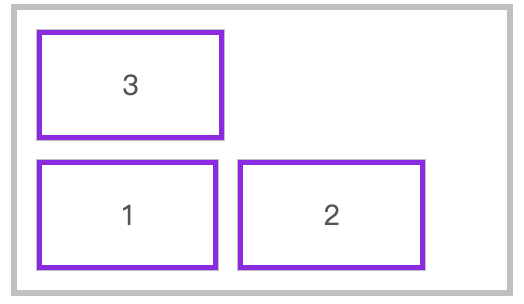
flex-direction: row;
flex-wrap: wrap-reverse;
2
垂直元素换行
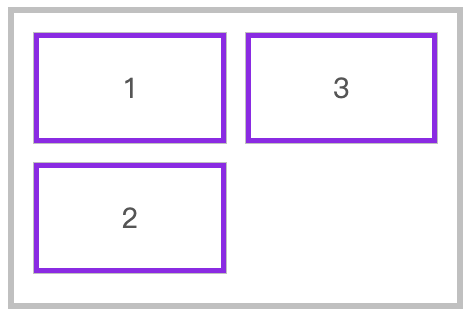
flex-direction: column;
flex-wrap: wrap;
2
垂直元素反向换行
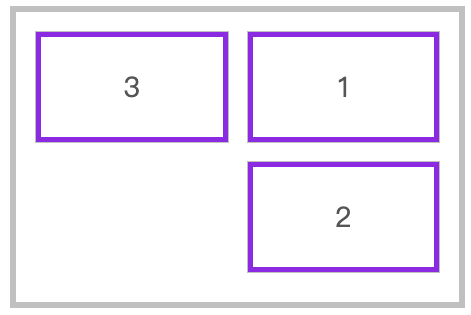
flex-direction: column;
flex-wrap: wrap-reverse;
2
flex-flow
📗 flex-flow 是 flex-direction 与 flex-wrap 的组合简写模式。
下面是从右向左排列,换行向上拆分行。
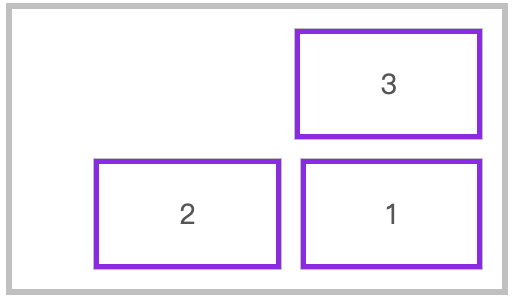
flex-flow: row-reverse wrap-reverse;
轴说明
水平排列
下面是使用 flex-flow: row wrap 的主轴与交叉轴说明。
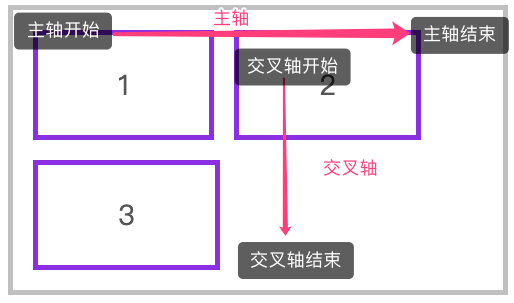
下面是使用 flex-flow: row-reverse wrap-reverse 的主轴与交叉轴说明。
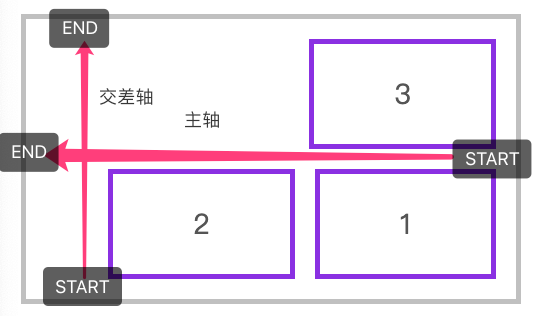
垂直排列
下面是使用 flex-flow: column wrap 的主轴与交叉轴说明。
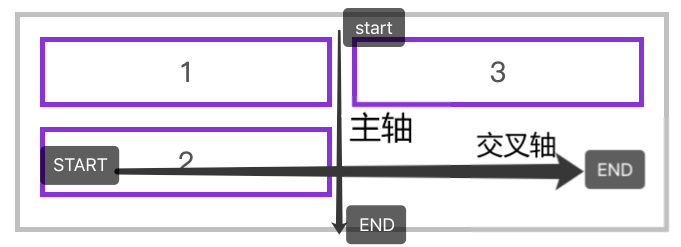
justify-content
📗 用于控制元素在主轴上的排列方式,再次强调是主轴的排列方式。
| 选项 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| flex-start | 元素紧靠主轴起点 |
| flex-end | 元素紧靠主轴终点 |
| center | 元素从弹性容器中心开始 |
| space-between | 第一个元素靠起点,最后一个元素靠终点,余下元素平均分配空间 |
| space-around | 每个元素两侧的间隔相等。所以,元素之间的间隔比元素与容器的边距的间隔大一倍 |
| space-evenly | 元素间距离平均分配 |
水平排列元素,并使用 justify-content: flex-end 对齐到主轴终点
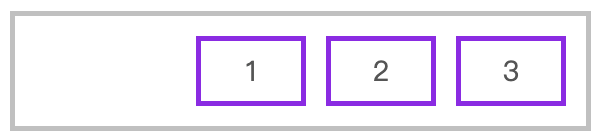
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
padding: 10px;
margin: 10px;
}
body {
font-size: 14px;
color: #555;
}
article {
border: solid 5px silver;
box-sizing: border-box;
display: flex;
flex-flow: row wrap;
/* 紧靠主轴尾 */
justify-content: flex-end;
}
article div {
width: 80px;
border: solid 5px blueviolet;
text-align: center;
font-size: 28px;
}
</style>
<article>
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
</article>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
使用 space-evenly 平均分配容器元素
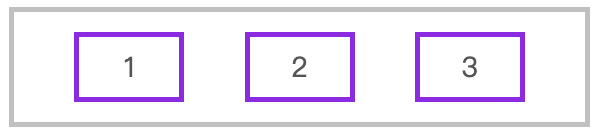
article {
border: solid 5px silver;
box-sizing: border-box;
display: flex;
flex-flow: row wrap;
justify-content: space-evenly;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
垂直排列时对齐到主轴终点

article {
height: 400px;
border: solid 5px silver;
box-sizing: border-box;
display: flex;
flex-flow: column wrap;
justify-content: flex-end;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
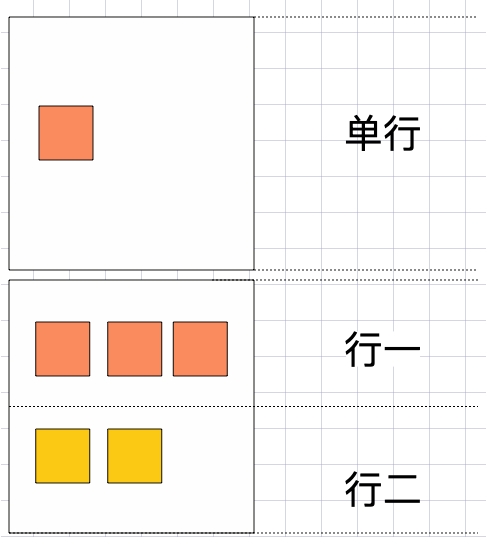
交叉轴行 👾
📗 元素在交叉轴上有行的概念,理解这个概念会对理解align-items与align-content有更好的帮助。
- align-item是控制元素在行上的排列
- align-content是控制行在交差轴上的排列(参考justify-content)
align-items
📗 用于控制容器元素在交叉轴(行)上的排列方式。
| 选项 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| stretch | 元素被拉伸以适应容器(默认) |
| center | 元素位于容器的中心 |
| flex-start | 元素位于容器的交叉轴开头 |
| flex-end | 元素位于容器的交叉轴结尾 |
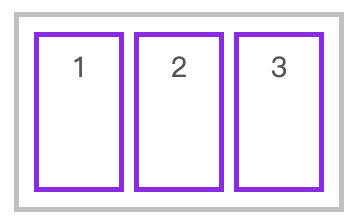
拉伸适应交叉轴
📌 如果设置了 width | height | min-height | min-width | max-width | max-height ,将影响stretch 的结果。(stretch的优先级高于width/height)
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
padding: 10px;
margin: 5px;
}
head {
display: block;
}
body {
font-size: 14px;
color: #555;
}
article {
height: 200px;
border: solid 5px silver;
box-sizing: border-box;
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
align-items: stretch;
}
article div {
width: 80px;
border: solid 5px blueviolet;
text-align: center;
font-size: 28px;
}
</style>
<article>
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
</article>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
对齐到交叉轴的顶部
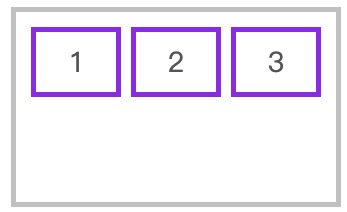
flex-direction: row;
align-items: flex-start;
2
对齐到交叉轴底部
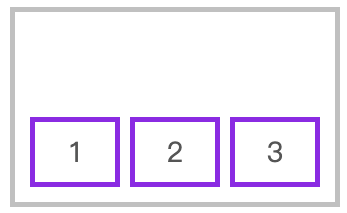
flex-direction: row;
align-items: flex-end;
2
对齐到交叉轴中心
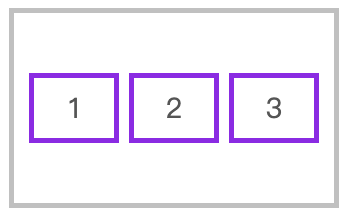
flex-direction: row;
align-items: center;
2
纵向排列时交叉轴排列
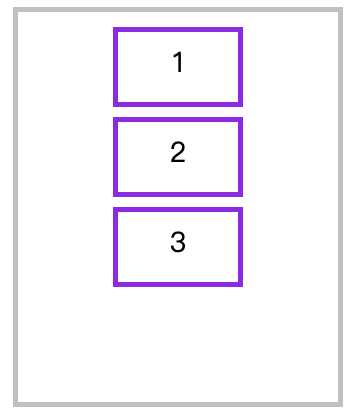
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
padding: 10px;
margin: 5px;
}
article {
height: 400px;
border: solid 5px silver;
box-sizing: border-box;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
}
article div {
height: 50px;
min-width: 100px;
border: solid 5px blueviolet;
text-align: center;
font-size: 28px;
}
</style>
<article>
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
</article>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
align-content
📗 只适用于多行显示的弹性容器,用于控制行(而不是元素)在交叉轴上的排列方式。
| 选项 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| stretch | 将空间平均分配给元素 |
| flex-start | 元素紧靠主轴起点 |
| flex-end | 元素紧靠主轴终点 |
| center | 元素从弹性容器中心开始 |
| space-between | 第一个元素靠起点,最后一个元素靠终点,余下元素平均分配空间 |
| space-around | 每个元素两侧的间隔相等。所以,项目之间的间隔比项目与边框的间隔大一倍 |
| space-evenly | 元素间距离平均分配 |
水平排列在交叉轴中居中排列
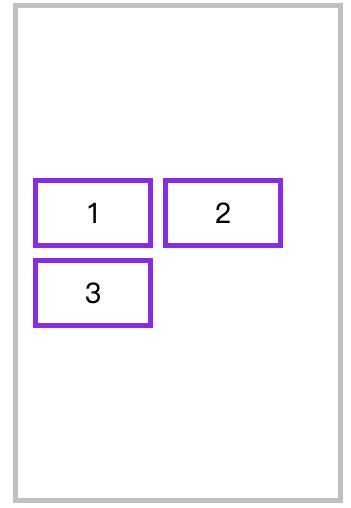
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
padding: 10px;
margin: 5px;
}
article {
height: 500px;
border: solid 5px silver;
box-sizing: border-box;
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
flex-wrap: wrap;
/* 单行内的元素在头部对齐 */
align-items: flex-start;
/* 所有行都在中间排列 */
align-content: center;
}
article div {
width: 90px;
border: solid 5px blueviolet;
text-align: center;
font-size: 28px;
}
</style>
<article>
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
</article>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
垂直排列时交叉轴的排列
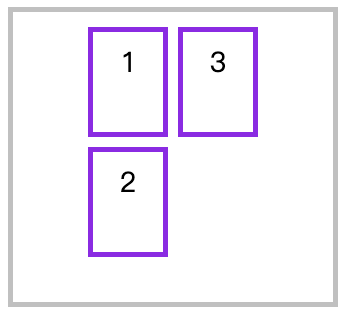
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
padding: 10px;
margin: 5px;
}
article {
height: 300px;
border: solid 5px silver;
box-sizing: border-box;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
flex-wrap: wrap;
align-items: flex-start;
/* 所有列都在中间排列 */
align-content: center;
}
article div {
min-width: 50px;
min-height: 80px;
border: solid 5px blueviolet;
text-align: center;
font-size: 28px;
}
</style>
<article>
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
</article>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
弹性元素
放在容器盒子中的元素即为容器元素。
- 不能使用float与clear规则
- 弹性元素均为块元素
- 绝对定位的弹性元素不参与弹性布局
📌 绝对定位的失去了原来的文档位置,而相对定位的元素还保留原来的文档位置
align-self
📗 用于控制单个元素在交叉轴上的排列方式,align-items 用于控制容器中所有元素的排列,而 align-self 用于控制一个弹性元素的交叉轴排列。
| 选项 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| stretch | 将空间平均分配给元素 |
| flex-start | 元素紧靠主轴起点 |
| flex-end | 元素紧靠主轴终点 |
| center | 元素从弹性容器中心开始 |
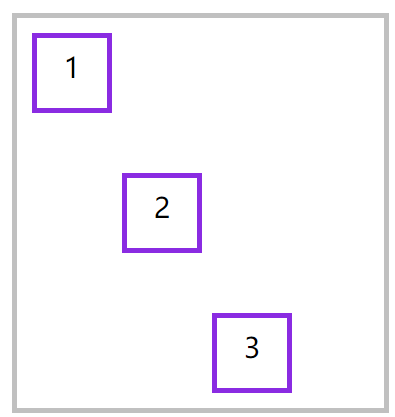
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
padding: 10px;
margin: 5px;
}
article {
height: 400px;
border: solid 5px silver;
box-sizing: border-box;
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
align-items: center;
}
article div {
height: 50px;
min-width: 50px;
border: solid 5px blueviolet;
text-align: center;
font-size: 28px;
}
article div:nth-of-type(1) {
align-self: flex-start;
}
article div:nth-of-type(3) {
align-self: flex-end;
}
</style>
<article>
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
</article>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
flex-grow
📗 用于将弹性盒子的可用空间,分配给弹性元素。可以使用整数或小数声明。

<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
body {
padding-left: 50px;
padding-top: 15px;
}
article {
border: solid 5px silver;
width: 550px;
height: 100px;
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
}
article * {
flex-grow: 1;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: blueviolet;
background-clip: content-box;
padding: 10px;
box-sizing: border-box;
font-size: 35px;
color: white;
}
</style>
<article>
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
</article>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
如果弹性元素设置了宽度,将把(弹性盒子-弹性元素宽度和)后按照 flex-grow 进行分配 。
下例中为三个DIV 弹性元素设置了1、3、6 ,即宽度分成10等份,第三个元素所占宽度为(宽度/(1+3+6)) X 6。
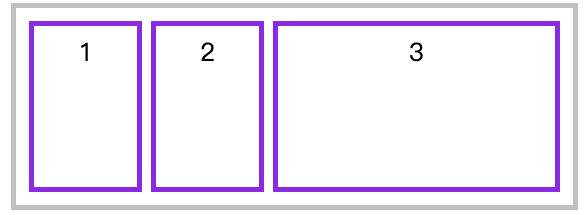
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
padding: 10px;
margin: 5px;
}
article {
width: 600px;
position: relative;
height: 200px;
border: solid 5px silver;
display: flex;
}
article div {
min-height: 80px;
border: solid 5px blueviolet;
text-align: center;
font-size: 28px;
}
article div:nth-of-type(1) {
width: 100px;
flex-grow: 1;
}
article div:nth-of-type(2) {
width: 100px;
flex-grow: 3;
}
article div:nth-of-type(3) {
width: 300px;
flex-grow: 6;
}
</style>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
flex-shrink
📗 与 flex-grow 相反 flex-shrink 是在弹性盒子装不下元素时定义的缩小值。
下例在600宽的弹性盒子中放了 1000 宽的弹性元素。并为最后两个元素设置了缩放,最后一个元素的缩放比例为 500 -( ( (1000-600) / (100X1+400x3+500X6) ) x 3 ) X 500 = 220.9,计算公式说明如下:
缩小比例 = 不足的空间 / (元素 1 宽度 x 缩小比例) + (元素 2 宽度 x 缩小比例) ...
最终尺寸 = 元素三宽度 - (缩小比例 x 元素 3 的宽度) X 元素宽度
2
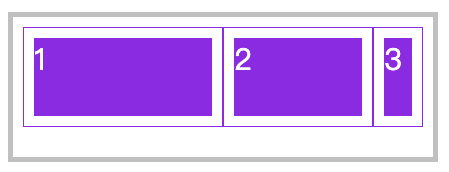
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
body {
padding-left: 50px;
padding-top: 15px;
}
article {
border: solid 5px silver;
width: 400px;
height: 120px;
display: flex;
padding: 10px;
box-sizing: content-box;
}
article div:nth-child(1) {
flex-shrink: 0;
}
article div:nth-child(2) {
flex-shrink: 1;
}
article div:nth-child(3) {
flex-shrink: 3;
}
article * {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
overflow: hidden;
background: blueviolet;
background-clip: content-box;
padding: 10px;
border: solid 1px blueviolet;
box-sizing: border-box;
font-size: 30px;
color: white;
}
</style>
<article>
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
</article>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
flex-basis
📗 flex-basis 属性定义了在分配多余空间之前,项目占据的主轴空间(main size)。浏览器根据这个属性,计算主轴是否有多余空间。
可以是长度单位,也可以是百分比。flex-basis的优先级高于width、height属性。
优先级
flex-basis 优先级大于 width、height。
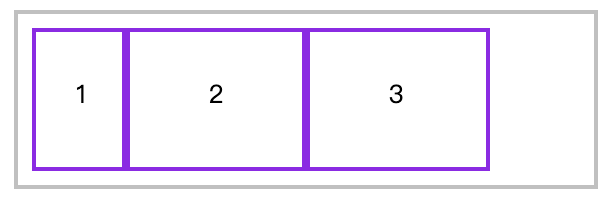
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
article {
width: 600px;
position: relative;
height: 150px;
margin-left: 100px;
margin-top: 100px;
outline: solid 5px silver;
display: flex;
padding: 20px;
}
article div {
outline: solid 5px blueviolet;
text-align: center;
font-size: 28px;
line-height: 5em;
}
article div:nth-of-type(1) {
flex-basis: 100px;
width: 200px;
}
article div:nth-of-type(2) {
flex-basis: 200px;
}
article div:nth-of-type(3) {
flex-basis: 200px;
}
</style>
<article>
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
</article>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
flex
📗 flex是flex-grow、flex-shrink 、flex-basis缩写组合。
建议使用 flex 面不要单独使用 flex-grow / flew-shrink / flex-basis 。
下例定义平均分配剩余空间,并不进行尺寸缩小,基础尺寸为200px。
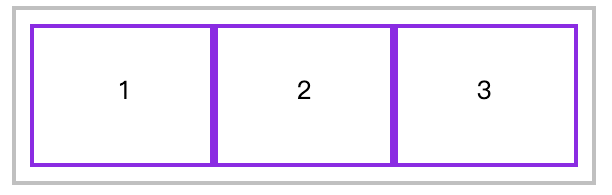
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
article {
width: 600px;
position: relative;
height: 150px;
margin-left: 100px;
margin-top: 100px;
outline: solid 5px silver;
display: flex;
padding: 20px;
}
article div {
outline: solid 5px blueviolet;
text-align: center;
font-size: 28px;
line-height: 5em;
/* stretch: 1(等比占有); strink: 0(不缩小); 100px(初始值) */
flex: 1 0 100px;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
order
📗 用于控制弹性元素的位置,默认为 order:0 数值越小越在前面,可以负数或整数。
下面是通过J动态改变order属性产生移动效果,因为本章节是讲CSS所以JS功能没有完善,只是体验一下order。

<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
body {
padding-left: 50px;
padding-top: 15px;
}
article {
border: solid 5px silver;
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
padding: 10px;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
article section {
order: 1;
flex: 1 0 100px;
padding: 10px;
background: blueviolet;
background-clip: content-box;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
text-align: center;
color: white;
}
article section div {
flex: 1;
}
article section div {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: center;
}
article section span {
flex: 0;
background: #000;
padding: 20px;
cursor: pointer;
}
</style>
<article>
<section>
<div>content1</div>
<span onclick="up(this)">up</span>
</section>
<section>
<div>content2</div>
<span onclick="up(this)">up</span>
</section>
</article>
<script>
function up(el) {
el.parentElement.style.order = getOrder(el.parentElement) * 1 - 1;
console.log(getOrder(el.parentElement))
}
function getOrder(el) {
return getComputedStyle(el, null).order;
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
弹性文本
文本节点也在弹性布局操作范围内。
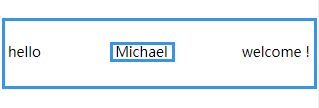
<style>
article {
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
justify-content: space-between;
height: 100vh;
align-items: center;
font-size: 14px;
}
</style>
<article>
hello
<span> Michael </span>
welcome !
</article>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
绝对定位
绝对定位的弹性元素不参与弹性布局(绝对定位的元素已经失去了原始的文档位置,而相对定位保持)
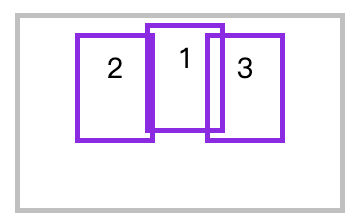
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
padding: 10px;
margin: 5px;
}
article {
position: relative;
height: 400px;
border: solid 5px silver;
box-sizing: border-box;
display: flex;
justify-content: space-evenly;
align-items: flex-start;
}
article div {
min-width: 50px;
min-height: 80px;
border: solid 5px blueviolet;
text-align: center;
font-size: 28px;
}
article div:nth-of-type(1) {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
}
</style>
<article>
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
</article>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
微信公众号
下面来开发类似微信公众号布局,包括底部二级菜单的弹性布局。
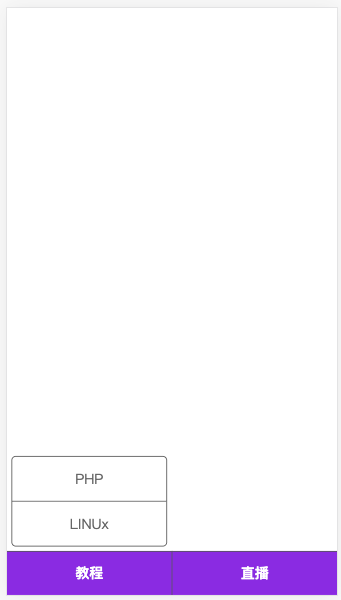
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
body {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
height: 100vh;
color: #666;
}
main {
flex: 1;
}
footer {
height: 50px;
background: blueviolet;
display: flex;
justify-content: space-evenly;
}
footer section {
display: flex;
flex: 1 0;
flex-direction: column-reverse;
border-right: solid 1px #555;
border-top: solid 1px #555;
}
footer section:last-child {
border-right: none;
}
footer section h4 {
flex: 0 0 50px;
display: flex;
text-align: center;
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: center;
cursor: pointer;
color: white;
}
footer section ul {
text-align: center;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
border: solid 1px #555;
margin-bottom: 5px;
border-radius: 5px;
margin: 5px;
}
footer section ul li {
flex: 1 0 50px;
border-bottom: solid 1px #555;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: center;
cursor: pointer;
}
footer section ul li:last-child {
border: none;
}
</style>
...
<main></main>
<footer>
<section>
<h4>教程</h4>
<ul>
<li>PHP</li>
<li>LINUx</li>
</ul>
</section>
<section>
<h4>直播</h4>
</section>
</footer>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
自动空间
在弹性布局中对元素使用margin-right:auto 等形式可以自动撑满空间。下例为第一个ul设置 margin-right:auto 表示右侧空间自动撑满,第二个ul靠近父元素右边界。(flex: 1也可以达到这个效果)

<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
.container {
width: 1200px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
nav {
display: flex;
border: solid 1px green;
margin-top: 20px;
align-items: center;
height: 60px;
box-shadow: 0 0 5px rgba(0, 0, 0, .2);
background: #f3f3f3;
}
ul {
list-style: none;
}
ul:nth-child(1) {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
margin-right: auto;
}
ul:nth-child(1)>li {
margin: 0 10px;
}
ul:nth-child(2)>li {
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
border-radius: 50%;
background: #9b59b6;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<nav>
<ul>
<li>文档</li>
<li>教程</li>
<li>视频</li>
<li>交流</li>
</ul>
<ul>
<li>
</li>
</ul>
</nav>
</div>
</body>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63