简单 Diff 算法
当新旧 vnode 的子节点都是一组节点时,为了以最小的性能开销完成更新操作,需要比较两组子节点,用于比较的算法就叫做 Diff 算法。
操作 DOM 的性能开销通常比较大,而渲染器的核心 Diff 算法就是为了解决这个问题而诞生的。
减少 DOM 操作的性能开销
🚀 核心 Diff 算法只关心新旧虚拟节点都存在一组子节点的情况。目前是暴力地卸载全部旧子节点,再挂载全部新子节点。这么做的确可以完成更新,但由于没有复用任何 DOM 元素,所以会产生极大的性能开销。
子节点更新的分析
新旧子节点数量相同:调用 patch 进行节点更新
新节点数量更多:有新节点需要挂载
旧节点数量更多:有旧节点需要卸载
在更新时,应该遍历其中长度较短的那一组,这样才能够尽可能多地调用 patch 函数进行更新。然后再处理节点的挂载与卸载。
function patchChildren(n1, n2, container) {
if (typeof n2.children === 'string') {
if (Array.isArray(n1.children)) {
n1.children.forEach((c) => unmount(c))
}
setElementText(container, n2.children)
} else if (Array.isArray(n2.children)) {
const oldChildren = n1.children
const newChildren = n2.children
const oldLen = oldChildren.length
const newLen = newChildren.length
const commonLength = Math.min(oldLen, newLen)
for (let i = 0; i < commonLength; i++) {
patch(oldChildren[i], newChildren[i])
}
// 如果 nextLen > prevLen,将多出来的元素添加
if (newLen > oldLen) {
for (let i = commonLength; i < newLen; i++) {
patch(null, newChildren[i], container)
}
} else if (oldLen > newLen) {
// 如果 prevLen > nextLen,将多出来的元素移除
for (let i = commonLength; i < oldLen; i++) {
unmount(oldChildren[i])
}
}
} else {
if (Array.isArray(n1.children)) {
n1.children.forEach(c => unmount(c))
} else if (typeof n1.children === 'string') {
setElementText(container, '')
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
DOM 复用与 Key 的作用
// oldChildren
[
{ type: 'p' },
{ type: 'div' },
{ type: 'span' }
]
// newChildren
[
{ type: 'div' },
{ type: 'span' },
{ type: 'p' }
]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
假设有新旧两组节点如上,因为节点数量相同,会执行三次的 patch 函数。
但是因为在遍历过程中,相同索引下节点 vnode.type 都不同,所以会执行 3 次卸载 3 次挂载,也就是 6 次 DOM 操作。
因为二者只是顺序不同,理想情况是通过移动来完成子节点的更新。前提是:新旧两组子节点中的确存在可复用的节点
// oldChildren
[
{ type: 'p', children: '1' },
{ type: 'p', children: '2' },
{ type: 'p', children: '3' }
]
// newChildren
[
{ type: 'p', children: '3' },
{ type: 'p', children: '1' },
{ type: 'p', children: '2' }
]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
我们发现这个案例可以通过移动完成更新。如果使用 vnode.type 判断可复用,由于 type 都相同,导致我们无法确定新旧两组子节点中节点的对应关系,也就无法得知应该怎样进行 DOM 移动才能完成更新。
因此,我们不能直接通过 vnode.type 来判断一个节点是否可复用。
// oldChildren
[
{ type: 'p', children: '1', key: 1 },
{ type: 'p', children: '2', key: 2 },
{ type: 'p', children: '3', key: 3 }
]
// newChildren
[
{ type: 'p', children: '3', key: 3 },
{ type: 'p', children: '1', key: 1 },
{ type: 'p', children: '2', key: 2 }
]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
所以我们需要引入额外的 key 来作为 vnode 的标识。这就好像虚拟节点的”身份证“号,只需要两个虚拟节点的 type 属性值和 key 属性值都是相同,那么我们就认为它们是相同的,即可以进行 DOM 的复用。
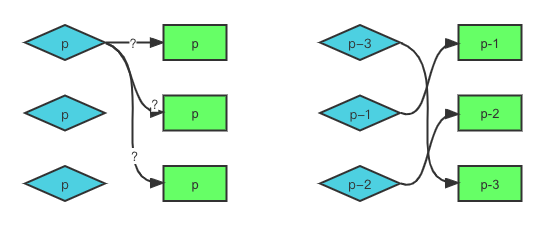
🔥 如果没有 key,我们无法知道新子节点与旧子节点间的映射关系,也就无法知道应该如何移动节点。有 key 的话情况不同,我们根据子节点的 key 属性,能够明确知道新子节点在旧子节点中的位置,这样就可以进行相应的 DOM 移动操作了。
📝 DOM 可复用只是 vnode 的 type 和 key 相同,但是仍旧需要对两个虚拟节点进行打补丁操作,因为内容是会变的。
function patchChildren(n1, n2, container) {
if (typeof n2.children === 'string') {
// ...
} else if (Array.isArray(n2.children)) {
const oldChildren = n1.children
const newChildren = n2.children
// 遍历新的 children
for (let i = 0; i < newChildren.length; i++) {
const newVNode = newChildren[i]
let j = 0
// 遍历旧的 children
for (j; j < oldChildren.length; j++) {
const oldVNode = oldChildren[j]
// 如果找到了具有相同 key 值的两个节点,则调用 `patch` 函数更新之
if (newVNode.key === oldVNode.key) {
patch(oldVNode, newVNode, container)
break // 这里需要 break
}
}
}
} else {
// ...
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
const oldVnode = {
type: 'div',
children: [
{ type: 'p', children: '1', key: 1 },
{ type: 'p', children: '2', key: 2 },
{ type: 'p', children: 'hello', key: 3 }
]
}
renderer.render(oldVnode, document.querySelector('#app'))
const newVnode = {
type: 'div',
children: [
{ type: 'p', children: 'world', key: 3 },
{ type: 'p', children: '1', key: 1 },
{ type: 'p', children: '2', key: 2 }
]
}
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('update')
renderer.render(newVnode, document.querySelector('#app'))
}, 400);
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
上面代码片段 render vnode 在执行更新是具体操作如下:
- 找到 key 为 3 的可复用节点,patch 函数将 DOM 文本内容由字符串 'hello' 更新为字符串 'world'
- 找到 key 为 1 的可复用节点,patch 函数无需任何操作
- 找到 key 为 2 的可复用节点,patch 函数无需任何操作
目前,所有节点对应的真实 DOM 元素都已经更新完毕,但 DOM 元素的顺序不变,还需要移动节点来完成真实 DOM 顺序的更新
找到需要移动的节点
目前已经实现可复用节点的匹配和打补丁,接下来就是找到需要移动的节点。
✅ 不需要移动节点:当两组子节点的节点顺序不变时,就不需要移动操作了。
取新的一组子节点中的第一个节点 p-3,它的 key 为 3。尝试在旧的一组子节点中找到具有相同 key 值的可复用节点,发现能够找到,并且该节点在旧的一组子节点中的索引为 2。
取新的一组子节点中的第一个节点 p-1,它的 key 为 1。尝试在旧的一组子节点中找到具有相同 key 值的可复用节点,发现能够找到,并且该节点在旧的一组子节点中的索引为 0。
节点 p-1 在旧 children 中的索引是 0,它小于节点 p-3 在旧 children 中的索引 2。这说明节点 p-1 在旧 children 中排在节点 p-3 的前面,但在新的 children 中,它排在节点 p-3 后面。因此,节点 p-1 对应的真实节点需要移动。
取新的一组子节点中的第一个节点 p-2,它的 key 为 2。尝试在旧的一组子节点中找到具有相同 key 值的可复用节点,发现能够找到,并且该节点在旧的一组子节点中的索引为 1。
节点 p-2 在旧 children 中的索引是 0,它小于节点 p-3 在旧 children 中的索引 2。这说明节点 p-2 在旧 children 中排在节点 p-3 的前面,但在新的 children 中,它排在节点 p-3 后面。因此,节点 p-2 对应的真实节点需要移动。
🔥 p-3 在旧 children 中的索引:在旧 children 中寻找具有相同 key 值节点的过程,遇到的最大索引值。
function patchChildren(n1, n2, container) {
if (typeof n2.children === 'string') {
// ...
} else if (Array.isArray(n2.children)) {
const oldChildren = n1.children
const newChildren = n2.children
// 遍历新的 children
for (let i = 0; i < newChildren.length; i++) {
const newVNode = newChildren[i]
let j = 0
// 遍历旧的 children
for (j; j < oldChildren.length; j++) {
const oldVNode = oldChildren[j]
// 如果找到了具有相同 key 值的两个节点,则调用 `patch` 函数更新之
if (newVNode.key === oldVNode.key) {
patch(oldVNode, newVNode, container)
if (j < lastIndex) {
// 需要移动
} else {
// 更新 lastIndex
lastIndex = j
}
break // 这里需要 break
}
}
}
} else {
// ...
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
在寻找到的可复用节点中,如果该节点在旧节点的索引比 lastIndex 小,那么这个节点对应的真实 DOM 节点就是需要移动的。同时,要保证 lastIndex 始终存储着当前遇到的最大索引值。
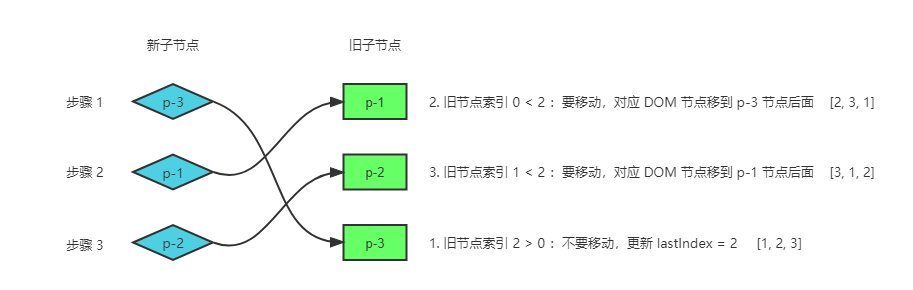
如何移动节点
参考上图,我们外层遍历的是新节点,新节点的顺序就是我们需要的 DOM 顺序。找到对应的可复用旧节点,将需要移动的节点到对应的新节点顺序即可。
节点 p-3,不用移动, lastIndex 更新为当前节点在旧节点中的索引 2。目前 DOM 为 [p-1, p-2, p-3]
节点 p-1,旧索引 0 小于 lastIndex,要移动,把对应的旧节点 p-1 移到 p-3后面,DOM 更新为 [p-2, p-3, p-1]
节点 p-2,旧索引 1 小于 lastIndex,要移动,把对应的旧节点 p-1 移到 p-3后面,DOM 更新为 [p-3, p-1, p-2]
function patchChildren(n1, n2, container) {
if (typeof n2.children === 'string') {
// ...
} else if (Array.isArray(n2.children)) {
const oldChildren = n1.children
const newChildren = n2.children
let lastIndex = 0
// 遍历新的 children
for (let i = 0; i < newChildren.length; i++) {
const newVNode = newChildren[i]
let j = 0
// 遍历旧的 children
for (j; j < oldChildren.length; j++) {
const oldVNode = oldChildren[j]
// 如果找到了具有相同 key 值的两个节点,则调用 `patch` 函数更新之
if (newVNode.key === oldVNode.key) {
patch(oldVNode, newVNode, container)
if (j < lastIndex) {
// 需要移动
const prevVNode = newChildren[i - 1]
if (prevVNode) {
const anchor = prevVNode.el.nextSibling
insert(newVNode.el, container, anchor)
}
} else {
// 更新 lastIndex
lastIndex = j
}
break // 这里需要 break
}
}
}
} else {
// ...
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
在移动过程中,我们需要获取当前 newVNode 节点的前一个虚拟节点,即 newChildren[i - 1],然后使用 insert 函数完成节点的移动:
insert(el, parent, anchor = null) {
parent.insertBefore(el, anchor)
}
2
3
添加新元素
当无法在旧节点中找到可复用节点时,也就是这个为新节点。那么要把这个节点插入到对应新节点的顺序位置当中:
const oldChildren = n1.children
const newChildren = n2.children
let lastIndex = 0
// 遍历新的 children
for (let i = 0; i < newChildren.length; i++) {
const newVNode = newChildren[i]
let j = 0
let find = false
// 遍历旧的 children
for (j; j < oldChildren.length; j++) {
const oldVNode = oldChildren[j]
// 如果找到了具有相同 key 值的两个节点,则调用 `patch` 函数更新之
if (newVNode.key === oldVNode.key) {
find = true
patch(oldVNode, newVNode, container)
if (j < lastIndex) {
// 需要移动
const prevVNode = newChildren[i - 1]
if (prevVNode) {
const anchor = prevVNode.el.nextSibling
insert(newVNode.el, container, anchor)
}
} else {
// 更新 lastIndex
lastIndex = j
}
break // 这里需要 break
}
}
if (!find) {
// 如果代码运行到这里,find 仍然为 false
// 说明当前 newVNode 没有在旧的一组子节点中找到可复用的节点
// 也就是说,当前 newVNode 是新增节点,需要挂载
const prevVNode = newChildren[i - 1]
let anchor = null
if (prevVNode) {
// 如果有前一个 vnode 节点,则使用它的下一个兄弟节点作为锚点元素
anchor = prevVNode.el.nextSibling
} else {
// 如果没有前一个 vnode 节点,说明即将挂载的新子节点是第一个节点
// 这是我们使用容器元素的 firstChild 作为锚点
anchor = container.firstChild
}
patch(null, newVNode, container, anchor)
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
移除不存在在的元素
遍历一次旧节点,如果无法在新节点列表中找到可复用的新节点,那么这些节点就是需要删除的节点。
// 遍历旧的节点
for (let i = 0; i < oldChildren.length; i++) {
const oldVNode = oldChildren[i]
// 拿着旧 VNode 去新 children 中寻找相同的节点
const has = newChildren.find(
vnode => vnode.key === oldVNode.key
)
if (!has) {
// 如果没有找到相同的节点,则移除
unmount(oldVNode)
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
总结
🔥 虚拟节点中 key 属性的作用:它就像虚拟节点的“身份证号”。在更新时,渲染器通过 key 属性找到可复用的节点,然后尽可能地通过 DOM 移动操作来完成更新,避免过多地对 DOM 元素进行销毁和重建。
简单 diff 算法寻找需要移动的节点:简单 diff 算法的核心逻辑是,拿新的一组子节点中的节点去旧的一组子节点中寻找可复用的节点。如果找到了,则记录该节点的位置索引。我们把这个位置索引成为做大索引。在整个更新过程中,如果一个节点的旧索引值小于最大索引,则说明该节点对应的真是 DOM 元素需要移动。